This post, consequently, delves into the concept of biodiversity hotspots in India, highlighting their immense significance, diverse locations, and the numerous challenges they face.
Furthermore, it explores how these regions contribute to global biodiversity and why their protection is crucial for future generations. India is a land of unparalleled diversity, not just in culture and languages but also in its rich natural heritage.
It is India is one of the 17 megadiverse countries in the world, hosting an incredible array of ecosystems, species, and landscapes. In addition to this, among its many ecological treasures are the biodiversity hotspot regions, which are recognized for their exceptional biological richness and endemism.
These hotspots, therefore, play a critical role in maintaining the ecological balance. This post, consequently, delves into the concept of biodiversity hotspots in India, highlighting their immense significance, diverse locations, and the numerous challenges they face.
Furthermore, it explores how these regions contribute to global biodiversity and why their protection is crucial for future generations.
What Are Biodiversity Hotspots?
Biodiversity hotspots are areas that are exceptionally rich in species diversity and are home to numerous endemic species those that are not found anywhere else in the world. Furthermore, to qualify as a biodiversity hotspot, a region must meet two criteria:
- It must have at least 1,500 species of vascular plants as endemics.
- It should have lost at least 70% of its original habitat.
Globally, there are 36 biodiversity hotspots, and India is home to four of them. These hotspots not only harbor unique flora and fauna but also play a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate, providing resources, and maintaining ecological balance.
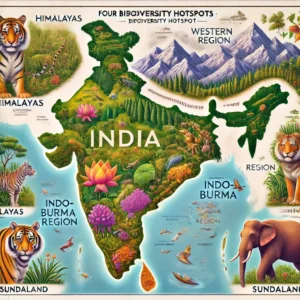
Biodiversity Hotspots in India
India boasts four biodiversity hotspots:
- The Himalayas
- The Western Ghats
- The Indo Burma Region
- The Sundaland (Nicobar Islands)
Each of these regions holds immense ecological and cultural importance.
1. The Himalayas
The Himalayas are one of the youngest and most dynamic mountain ranges in the world. Spanning across several states, including Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and parts of northeastern India, this region is a biodiversity hotspot teeming with life.
- Flora and Fauna:
The Himalayan region is home to unique species like the snow leopard, red panda, Himalayan monal, and blue poppy. Moreover, the forests here range from tropical to alpine, with rhododendrons, oaks, and pines dominating the landscape. - Endemism:
Several species, such as the Himalayan musk deer and the Himalayan wolf, are found exclusively in this region. - Conservation Challenges:
The Himalayas face threats from deforestation, climate change, and unregulated tourism. Glacial retreat is another significant issue impacting the region’s ecology.
2. The Western Ghats
The Western Ghats, also known as the Sahyadri Hills, stretch along the western coast of India, passing through states like Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu. This region is a UNESCO World Heritage Site due to its ecological and cultural significance.
- Flora and Fauna:
This hotspot is known for its evergreen forests, home to species like the Malabar civet, lion tailed macaque, and Nilgiri tahr. The region is also rich in plant diversity, with many medicinal and endemic plants. - Endemism:
Nearly 50% of the amphibian species found here are endemic, along with many reptiles and plants. - Conservation Challenges:
Urbanization, agricultural expansion, and habitat fragmentation pose significant threats. Hydroelectric projects and mining have also impacted the region.
3. Indo Burma Region
The Indo Burma region covers northeastern India, including states like Assam, Meghalaya, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura, and Nagaland. It extends into neighboring countries, making it one of the most biologically diverse areas in the world.
- Flora and Fauna:
This region boasts tropical and subtropical forests, home to species like the hoolock gibbon, pygmy hog, and golden langur. The forests are also rich in bamboo and orchids. - Endemism:
Many species, such as the Manipur bush rat and the Arunachal macaque, are exclusive to this area. - Conservation Challenges:
Shifting cultivation, illegal wildlife trade, and deforestation are significant issues. Moreover, political instability and lack of stringent conservation policies exacerbate these challenges.
4. Sundaland (Nicobar Islands)
The Sundaland hotspot includes the Nicobar Islands, located in the Bay of Bengal. In addition, these islands are part of the larger Sundaland region, which extends to parts of Indonesia and Malaysia.
- Flora and Fauna:
The Nicobar Islands are home to unique species such as the Nicobar megapode, crab eating macaque, and saltwater crocodile. The mangroves and coral reefs here are particularly noteworthy. - Endemism:
The islands host several endemic bird and reptile species, making them a crucial area for biodiversity conservation. - Conservation Challenges:
The region is vulnerable to rising sea levels, habitat destruction, and invasive species. Furthermore, the 2004 tsunami caused significant ecological damage, highlighting the fragility of this ecosystem.
Importance of Biodiversity Hotspots
Biodiversity hotspots are not just ecological treasures; they are vital for human survival. These regions provide ecosystem services such as:
- Climate Regulation: Forests in these hotspots act as carbon sinks, mitigating climate change.
- Water Resources: They play a crucial role in the hydrological cycle, ensuring water availability.
- Medicinal Resources: Many plants from these regions are used in traditional and modern medicine.
- Cultural Significance: Indigenous communities in these areas rely on natural resources for their livelihoods and traditions.
Threats to Biodiversity Hotspots
Despite their importance, biodiversity hotspots face numerous threats:
- Deforestation: Expanding agriculture and urbanization, consequently, lead to habitat destruction.
- Climate Change: As a result, rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns disrupt ecosystems.
- Pollution: Industrial and agricultural pollutants harm soil, water, and air quality.
- Poaching and Illegal Trade: Wildlife trafficking poses a severe threat to many species.
- Invasive Species: Furthermore, non native species often outcompete native flora and fauna, disrupting the ecological balance.
Conservation Efforts in India
India has undertaken several initiatives to protect its biodiversity hotspots. Some of these include:
- Protected Areas: Establishment of national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and biosphere reserves.
- Legislation: Laws like the Wildlife Protection Act (1972) and the Forest Conservation Act (1980) aim to safeguard ecosystems.
- Community Involvement: Programs like Joint Forest Management (JFM) involve local communities in conservation.
- Biodiversity Management Committees (BMCs): Specifically, these are formed under the Biological Diversity Act, 2002, to promote the sustainable use of resources.
- International Collaboration: India is a signatory to several international agreements like the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
How Can You Contribute?
Protecting biodiversity is a collective responsibility. Here are some ways you can help:
- Support Conservation Organizations: Donate to or volunteer with groups working to protect biodiversity.
- Reduce Your Carbon Footprint: Use energy efficient appliances, opt for public transport, and reduce waste.
- Promote Sustainable Practices: Encourage the use of eco friendly products and support sustainable tourism.
- Educate Others: Spread awareness about the importance of biodiversity and the threats it faces.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are biodiversity hotspots?
Biodiversity hotspots are regions with high species diversity and a significant number of endemic species. They are also areas that have lost at least 70% of their original habitat.
Q2. How many biodiversity hotspots are there in India?
Additionally, the Indo Burma region is diverse, and finally, the Sundaland offers coastal ecosystems.
Q3. Why are biodiversity hotspots important?
These regions are crucial for maintaining ecological balance; furthermore, they regulate climate and provide essential resources such as water, food, and medicine.
Q4. What are the major threats to biodiversity hotspots in India?
The primary threats include deforestation, climate change, pollution, poaching, and invasive species.
Q5. How can we protect biodiversity hotspots?
Conservation efforts, such as creating protected areas, enforcing laws, and involving local communities, are essential. Additionally, promoting sustainable practices can further help safeguard these regions.